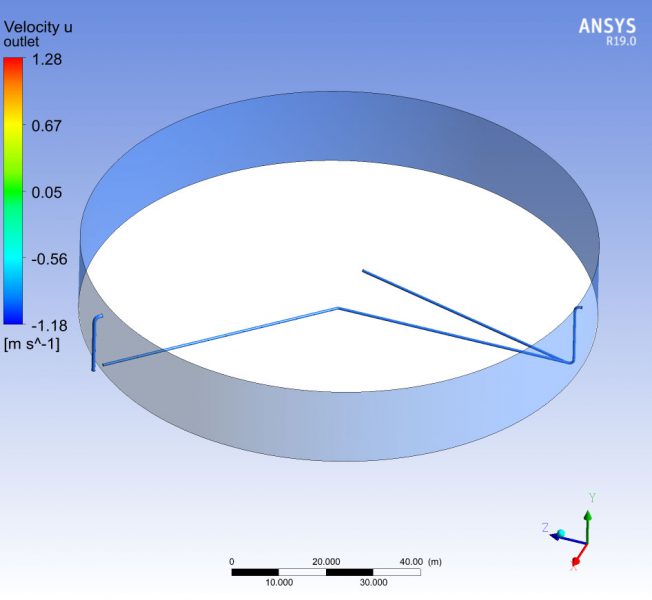
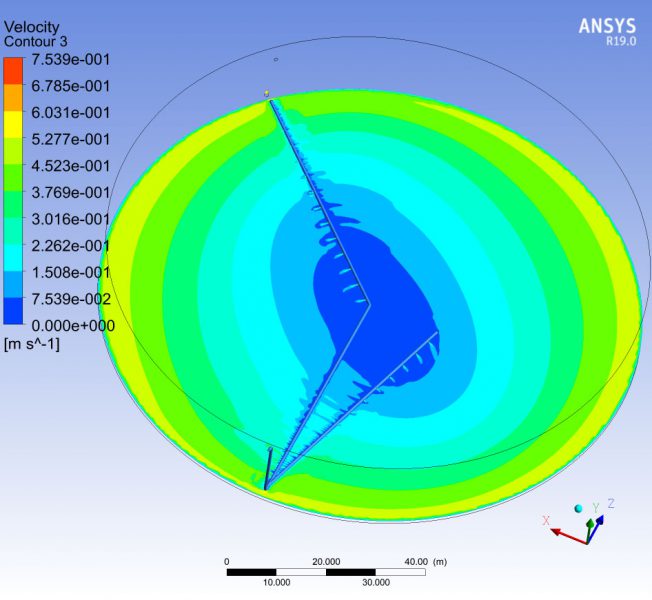
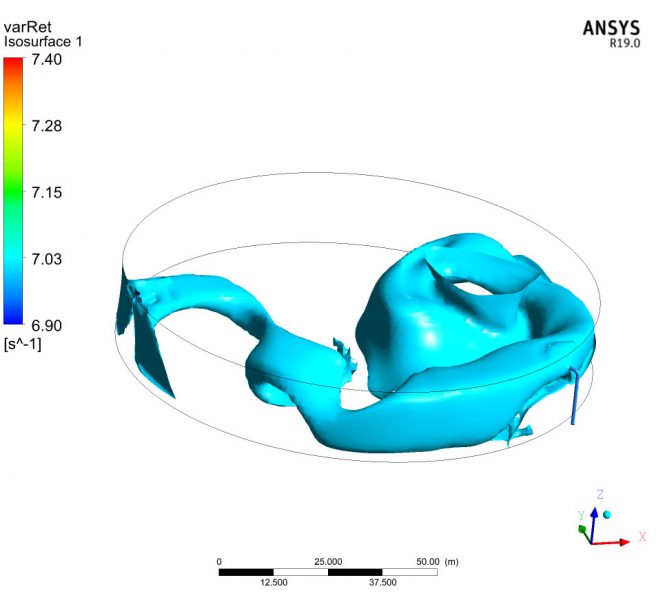
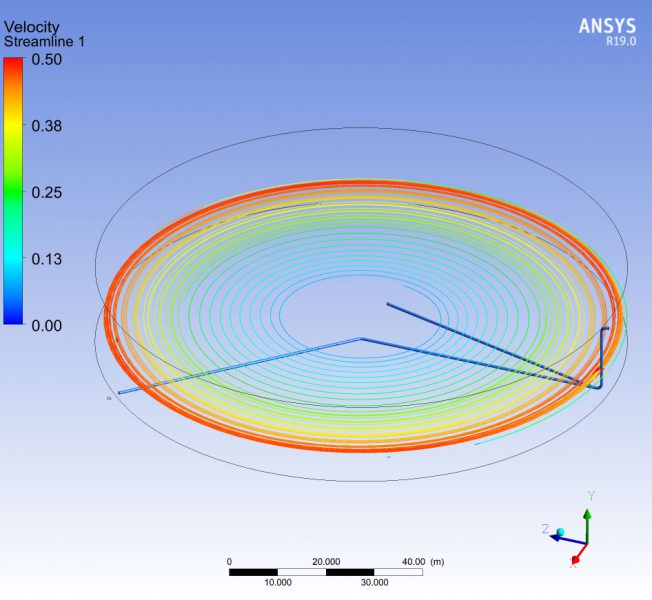
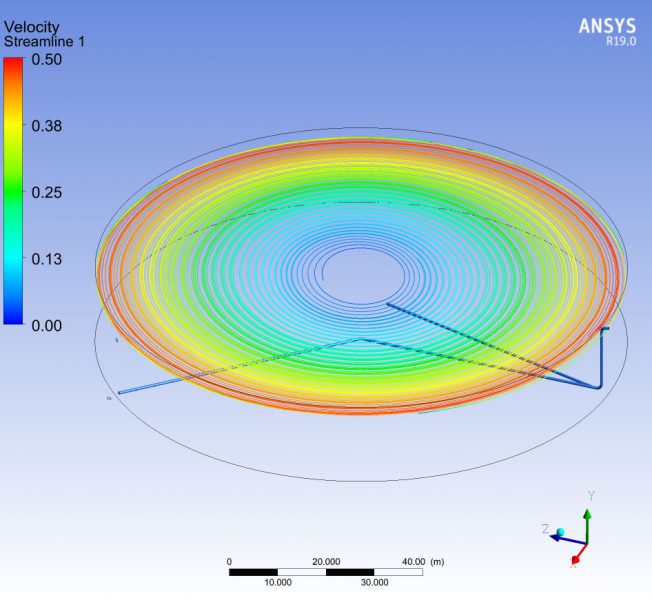
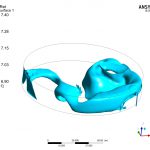
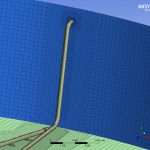
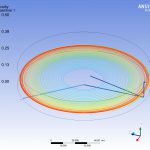
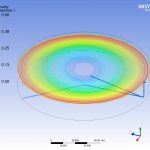
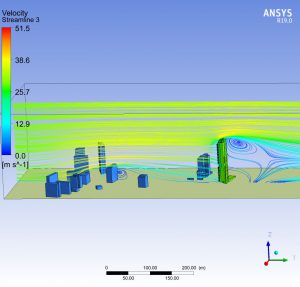
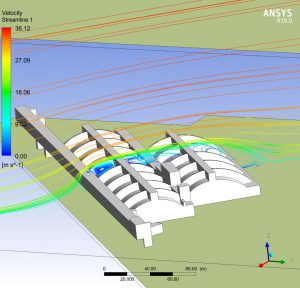
The time spent by each particle of water in transit through the storage tank is a parameter to be controlled, since it has a direct influence on the quality of the water. The study also tries to establish if according to the kinematics of the movement of the fluid, areas of the deposit could remain at rest, without the capacity to renew.
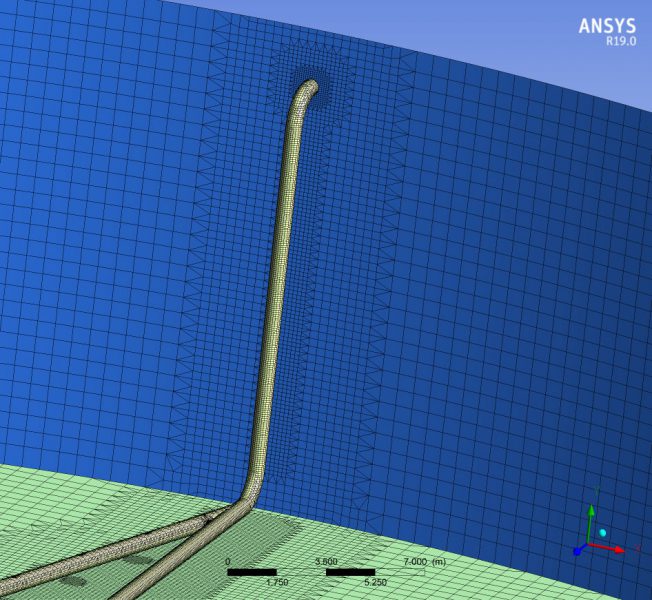
The use of numerical techniques allows to design beforehand with sufficient technical guarantees, imposing as an alternative method to the real test in the laboratory, which involves a higher cost and term. MC2 has developed several numerical simulations RANS type of fluid dynamics (Computing Fluid Dynamics, CFD), to evaluate the maximum retention time of all the fluid particles circulating in the tank., in order to validate its design.The simulations have been verified successfully by reproducing other cases already resolved.